In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern medicine, innovative healthcare trends are reshaping patient care in profound ways. As technology advances and societal needs shift, healthcare providers and stakeholders are increasingly focusing on transforming the patient experience through innovative solutions. This article explores the key trends revolutionizing healthcare delivery, improving outcomes, and redefining the patient-provider relationship.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, particularly evident during the COVID-19 pandemic. By leveraging digital platforms, patients can now access medical consultations from the comfort of their homes. This trend not only enhances convenience but also reduces the burden on healthcare facilities and lowers the risk of exposure to infectious diseases.
Remote monitoring, often integrated with telemedicine, involves using wearable devices and mobile applications to track patients’ health metrics in real-time. These technologies allow healthcare providers to monitor chronic conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, more effectively. By analyzing data collected from these devices, clinicians can make timely interventions and adjust treatment plans based on real-time information.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing healthcare by improving diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, and optimizing operational efficiency. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data, including imaging studies and patient records, to assist in diagnosing diseases with greater precision.
Machine learning models are increasingly being used to predict patient outcomes and identify at-risk individuals before symptoms arise. For instance, AI-powered tools can predict the likelihood of readmission for patients with chronic conditions, allowing healthcare providers to implement preventive measures and reduce hospital readmissions.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine, also known as precision medicine, focuses on tailoring healthcare treatments to individual patients based on their genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Advances in genomics and biotechnology have enabled healthcare professionals to develop targeted therapies that are more effective and have fewer side effects compared to traditional treatments.
Genetic testing and biomarkers play a crucial role in personalized medicine. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, healthcare providers can predict their susceptibility to certain diseases, customize drug dosages, and select the most appropriate treatment options. This approach not only enhances treatment efficacy but also minimizes adverse reactions and improves patient outcomes.
Digital Health Records and Interoperability
The adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) has transformed the way patient information is stored and shared. EHRs enable healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient histories, facilitating more informed decision-making and coordination of care. However, the full potential of EHRs can only be realized through interoperability—the ability of different EHR systems to exchange and interpret shared data seamlessly.
Interoperability is crucial for creating a cohesive healthcare ecosystem where information flows smoothly between providers, patients, and healthcare organizations. Initiatives such as Health Information Exchanges (HIEs) and standardized data formats are working towards achieving greater interoperability, ultimately leading to improved patient care and more efficient healthcare delivery.
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are making significant strides in healthcare, offering innovative solutions for training, treatment, and patient engagement. VR is being utilized for medical education and surgical training, providing a risk-free environment for practitioners to practice complex procedures and refine their skills.
AR, on the other hand, is enhancing surgical precision by overlaying digital information onto the real world. Surgeons can use AR to visualize anatomical structures and guide their actions during procedures, improving accuracy and reducing the risk of errors. Additionally, AR is being explored as a tool for patient education, helping individuals understand their conditions and treatment options more effectively.
Wearable Technology and Health Apps
Wearable technology, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, has become a ubiquitous part of modern life. These devices are equipped with sensors that monitor various health parameters, including heart rate, physical activity, and sleep patterns. The data collected from wearables can be synchronized with health apps, allowing users to track their health and make informed lifestyle choices.
Healthcare providers are increasingly integrating wearable technology into patient care plans, using the data to monitor progress and detect potential health issues early. Wearables also empower patients to take an active role in managing their health, fostering greater engagement and adherence to treatment regimens.
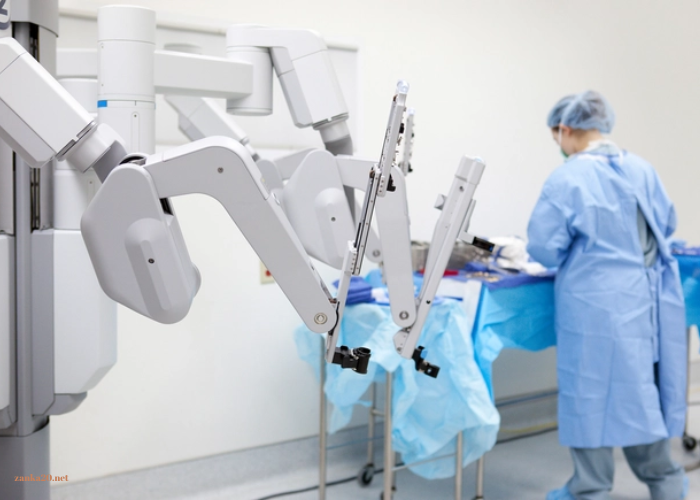
Robotics and Automation
Robotic technology and automation are transforming various aspects of healthcare, from surgical procedures to administrative tasks. Robotic-assisted surgery allows for minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision and reduced recovery times. These advanced systems provide surgeons with greater control and visibility, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Automation is also streamlining administrative processes, such as appointment scheduling, billing, and inventory management. By reducing the administrative burden on healthcare professionals, automation frees up valuable time that can be redirected towards patient care, ultimately improving overall efficiency and patient satisfaction.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, commonly associated with cryptocurrencies, is finding applications in healthcare due to its ability to securely and transparently manage data. In healthcare, blockchain can be used to create immutable records of patient information, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized access.
Blockchain also has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management, enhancing the traceability and security of pharmaceuticals and medical supplies. By providing a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger, blockchain technology can improve the safety and reliability of healthcare operations.
Patient-Centered Care and Experience
The focus on patient-centered care has gained momentum, emphasizing the importance of addressing patients’ needs, preferences, and values. This approach involves involving patients in their care decisions, enhancing communication, and providing emotional support.
Innovative healthcare trends are aligning with the principles of patient-centered care by offering personalized treatment options, improving accessibility, and enhancing the overall patient experience. Initiatives such as patient portals, personalized care plans, and feedback mechanisms are contributing to a more holistic and patient-focused approach to healthcare.
Conclusion
The landscape of healthcare is undergoing a remarkable transformation driven by innovative trends that are reshaping patient care. From telemedicine and AI to personalized medicine and wearable technology, these advancements are improving diagnostic accuracy, enhancing treatment options, and empowering patients to take control of their health.
As these trends continue to evolve, they hold the promise of a more efficient, effective, and patient-centered healthcare system. Embracing these innovations and integrating them into healthcare practices will be crucial in addressing the challenges of modern medicine and delivering high-quality care to patients worldwide.




Leave a Reply